最近工作中接触到PostgreSQL,所以稍微学习下它的几种数据类型:json、jsonb、数组以及相对应的数据查询。
PostgreSQL中单引号用于表示字符串值,双引号用于表示系统标识符,没有反引号`。
JSON、JSONB
json和jsonb的异同
在PostgreSQL中,json和jsonb都是用来存储json数据的。
使用json类型时,PostgreSQL会将输入的json文本存储起来,包括其中的空格以及键的顺序,在查询使用时才去解析。而jsonb类型会将输入的json文本解析为对应的二进制数据进行存储。jsonb类型相较json类型而言更高效,性能更好,且支持建立索引。
json及jsonb的相关SQL操作
表的创建
-- 创建测试表
CREATE TABLE test (
id int not null primary key,
attr_json json not null,
attr_jsonb jsonb not null
);
数据插入
INSERT INTO test (id, attr_json, attr_jsonb)
VALUES (1, '{"name":"anhoder","age":18}', '{"name":"anhoder","age":18}'),
(2, '{"name":"jane","age":34,"son": {"name":"coco","age":1}}', '{"name":"jane","age":34,"son": {"name":"coco","age":1}}'),
(3, '{"name":"alan","age":35,"son": {"name":"coney","age":1}}', '{"name":"alan","age":35,"son": {"name":"coney","age":1}}'),
(4, '{"name":"jojo","age":26}', '{"name":"jojo","age":26}');
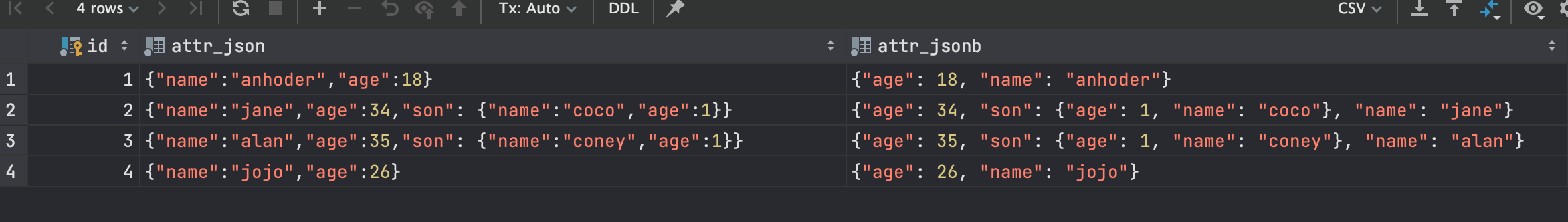
插入后的结果:
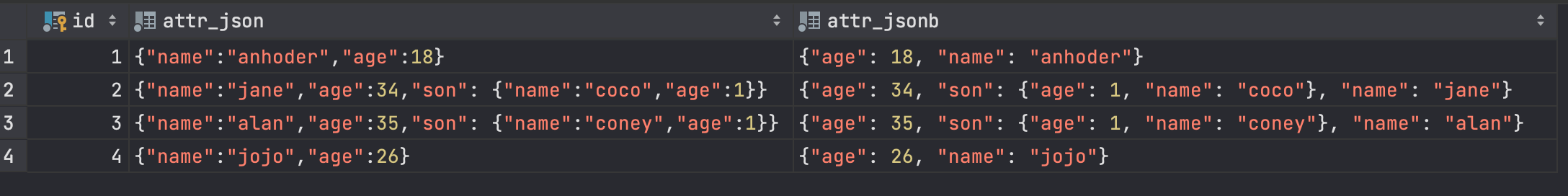
可见jsonb会对数据进行解析后,再进行存储,json则存储原输入。
数据查询
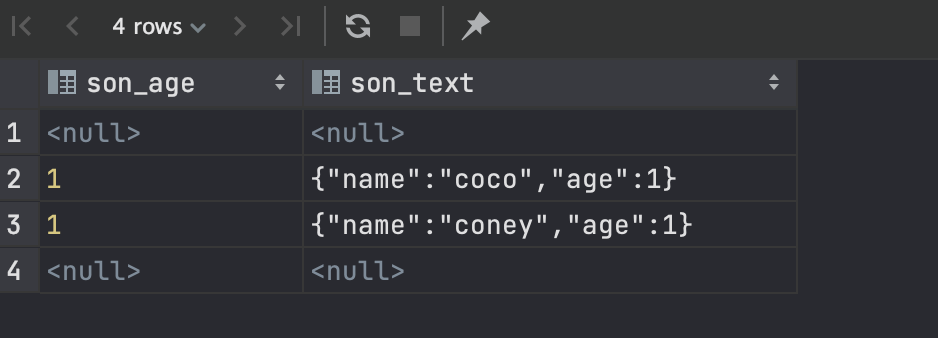
-- -> 获取对象的属性,结果作为json对象;->>获取对象的属性,结果作为文本
select attr_json->'son'->'age' as son_age, attr_json->>'son' as son_text from test;
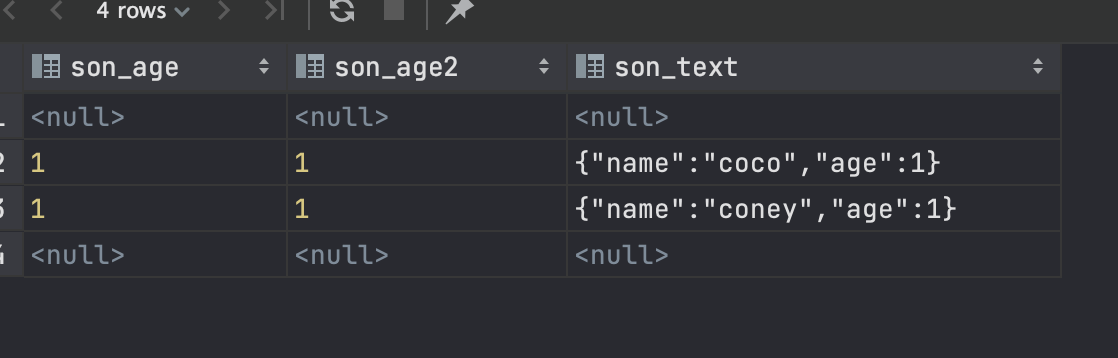
-- #> 根据路径获取结果作为json对象;#>> 根据路径获取结果作为文本(json, jsonb结果一致)
select attr_json#>'{son}'->'age' as son_age, attr_json#>'{son,age}' as son_age2, attr_json#>>'{son}' as son_text from test;
-- @>左边是否包含右边;<@右边是否包含左边 (jsonb可用)
select * from test where attr_jsonb@>'{"age":18}';
-- ? 是否存在属性
select * from test where attr_jsonb ? 'name';
-- ?| 存在数组中任意一个属性则为true (jsonb可用)
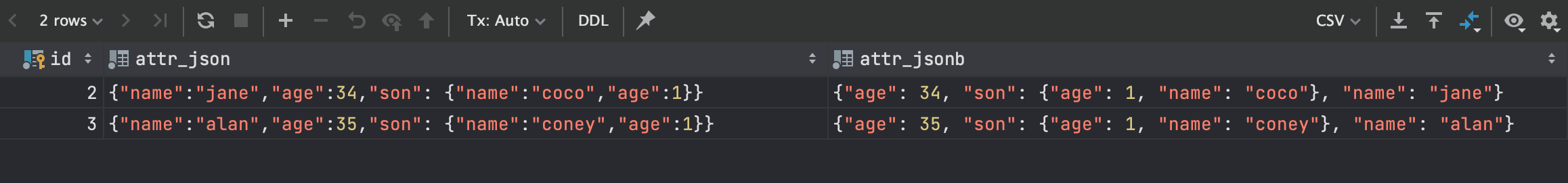
select * from test where attr_jsonb ?| array ['son', 'name'];
-- ?& 同时存在数组中的所有属性则为true (jsonb可用)
select * from test where attr_jsonb ?& array ['son', 'name'];
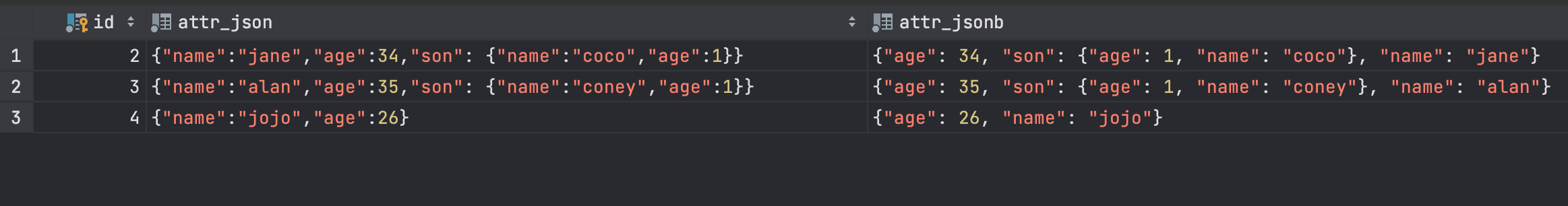
-- ::为类型转换
select * from test where (attr_json->>'age')::int>20;
数据更新
-- jsonb_set(jsonb old_jsonb, text[] path, jsonb new_jsonb, bool create_if_missing) 更新jsonb
update test set attr_jsonb=jsonb_set(attr_jsonb, '{son}', '{"name":"con","age":2}')
where (attr_jsonb#>>'{son,name}') = 'coco';
-- 根据路径删除属性 (jsonb可用)
update test set attr_jsonb=attr_jsonb#-'{son,name}';
-- 删除属性 (jsonb可用)
update test set attr_jsonb=attr_jsonb-'son' where attr_jsonb ? 'son';
数组
-- 创建测试表
CREATE TABLE test_arr (
id int not null primary key,
arr int[] not null
);
-- 插入数据
insert into test_arr (id, arr) values (1, array[2,3,4]),(2, array[3,4,5]);
-- 数组合并
select array[1,2,3,4] || array[2,3,4,5]; -- 结果:{1,2,3,4,2,3,4,5}
select 2 || array[2,3,4,5]; -- 结果:{2,2,3,4,5}
-- 数组比较,每个元素依次比较大小
select array[1,2,3,4] > array[1,2,3]; -- 结果: true
select array[1,2,3,4] > array[1,2,4]; -- 结果: false
-- 数组包含关系
select array[1,2,3] @> array[2,3]; -- 结果: true
select array[1,2,3] @> array[2,3,4]; -- 结果: false
-- 数组是否有共同元素
select array[1,2,3] && array[3,4,5]; -- 结果: true
